What is CCT or Kelvin in Lights?
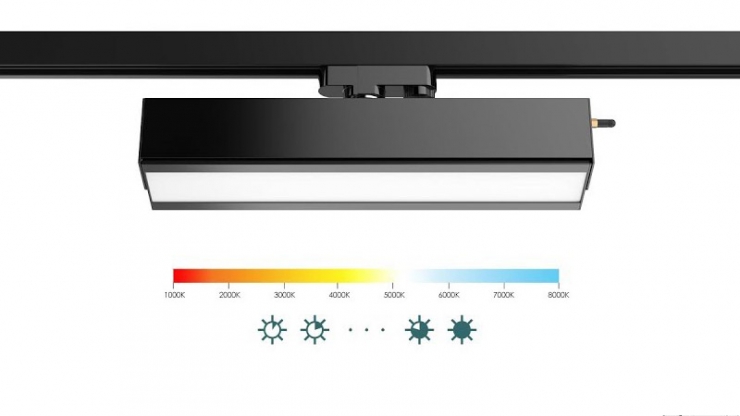

CCT, or Correlated Color Temperature, serves as an indicator used to categorize the color of a light source. It represents the color of visible light emitted by the source. As objects heat up, they emit light, and their colors change based on temperature, from orange and yellow to blue. Color temperature is measured in Kelvin (K) and reflects the heat of a black object, providing a color tone similar to the light source.
Kelvin, an international temperature unit like Celsius, considers absolute zero as -273.15 °C. Conversion from Celsius to Kelvin is achieved through the formula [K] = [°C] + 273.15. Color temperature is expressed in Kelvin, denoted by the symbol K, and is commonly used in the lighting sector, photography, and publishing.
In lighting, color temperature categorizes shades of white, where lower Kelvin values result in warmer, more orange tones, while higher values yield cooler, bluer hues. Common color temperatures range from 1000 K to 12,000 K. Warm white (2700 K – 3500 K) is suitable for spaces like living rooms, bedrooms, and restaurants, while cold white (4500 K – 6500 K) is preferred in offices, work areas, and learning spaces.

Different color temperatures offer various advantages. Warm white lightings create a relaxing atmosphere, while cold white lightings contribute to increased concentration. The choice of color temperature depends on the specific usage area and its purpose.
 LED Bulbs
LED Bulbs Downlights
Downlights Tube Rod
Tube Rod Batten Light
Batten Light Panel Lights
Panel Lights Flood Light
Flood Light Rope Light
Rope Light Strip Light
Strip Light Solar Street Light
Solar Street Light Integrated
Integrated Track Light
Track Light Highbay Lights
Highbay Lights Canopy Lights
Canopy Lights Garden Light
Garden Light Emergency Lights
Emergency Lights
 Ceiling Fan
Ceiling Fan Pedestal Fan
Pedestal Fan Louver Fan
Louver Fan Bracket Fan
Bracket Fan Exhaust Fan
Exhaust Fan Table Fan
Table Fan Misting Fan
Misting Fan
 Glamor Series
Glamor Series Star Series
Star Series Rose Gold Series
Rose Gold Series Aluminium Series
Aluminium Series
 PPRC Pipes & Fittings
PPRC Pipes & Fittings U-PVC Pipes & Fittings
U-PVC Pipes & Fittings U-PVC Ducts
U-PVC Ducts
 Electric Heaters
Electric Heaters
 Lear Circuit Breaker
Lear Circuit Breaker PVC Tape
PVC Tape
